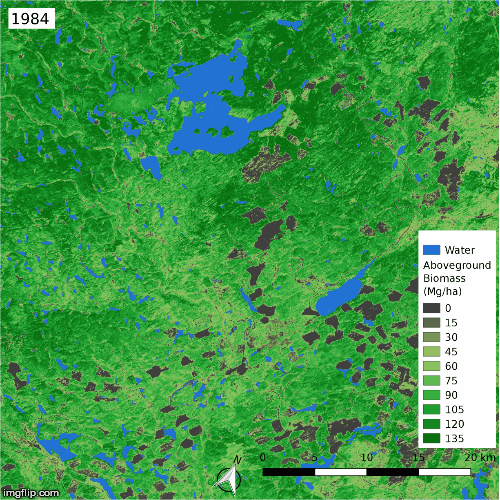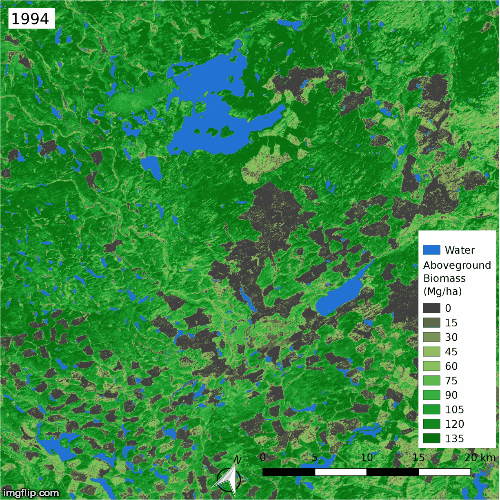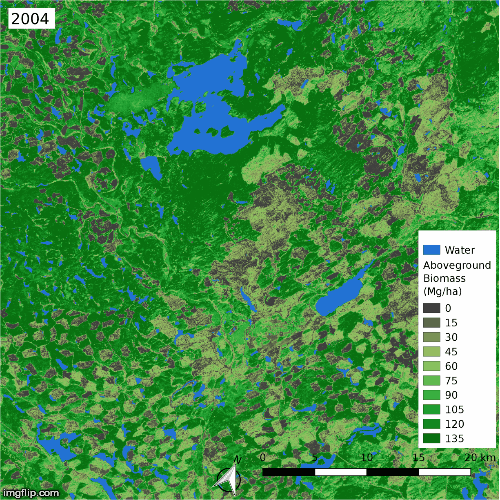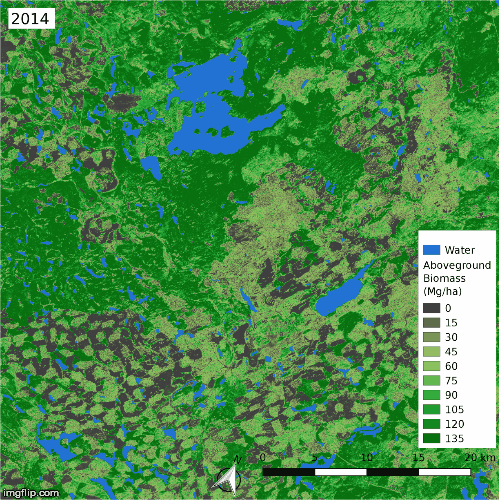
Land cover changes over the ABoVE domain, mapped with high-resolution imagery and Landsat time series. [Wang et al. (2020)]
Time series of aboveground biomass in a heavily harvested region in British Columbia, estimated from spaceborne lidar and Landsat time series [Wang et al. (2021)]
Arctic-Boreal Ecosystems
As part of NASA’s Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE), we analyzed dense time series of Landsat imagery to identify extensive land cover change across Arctic-Boreal North America, with disturbances spurring the replacement of evergreen forests by deciduous forests and the expansion of arctic shrubs. These land cover changes drive much of the greening and browning trends in northern Canada and Alaska, adding some nuance to our understanding of satellite-derived trends in ecosystem productivity in the far north. We then combined Landsat with spaceborne lidar data to estimate the aboveground biomass dynamics and found that fires are strongly suppressing the regional carbon sink. This work was reported on by Science Friday.
A currently funded ABoVE project will expand this work to the entirety of Canada and Alaska.
Selected relevant publications: